| Version 3 (modified by , 13 years ago) (diff) |
|---|
This guide is intended to get you up and running in TortoiseGit for Windows. It will take you through installation, and key creation.
Note: this guide was created on a 32-bit Windows XP SP2 machine. Some steps may differ slightly on other operating systems. In particular, most Vista and Windows 7 machines are 64-bit rather than 32-bit, so you will need the 64-bit version of TortoiseGit (linked in the instructions below).
Installation
Git for Windows
Git is the software that talks to the remote repository, tracks your local changes, and so forth.
Start by downloading Git for Windows 1.7.11 and TortoiseGit 1.7.11.3 (32-Bit or 64-Bit)
You should have the following files when you're done:
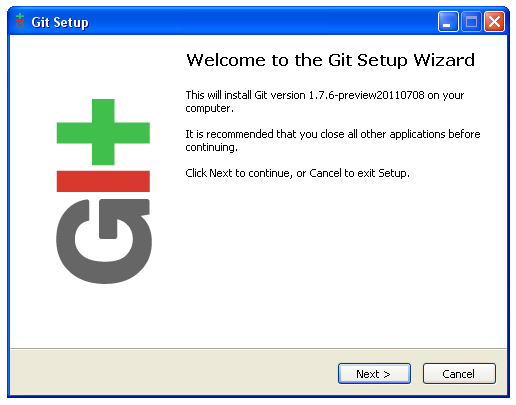
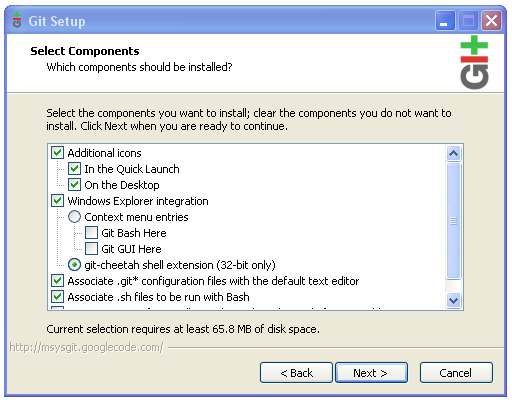
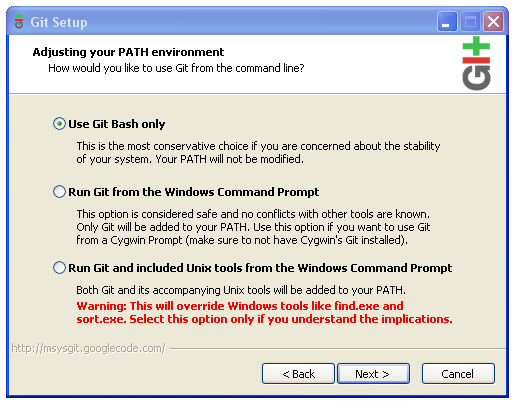
Run Git-1.7.11-preview20120710.exe to start Git installation.
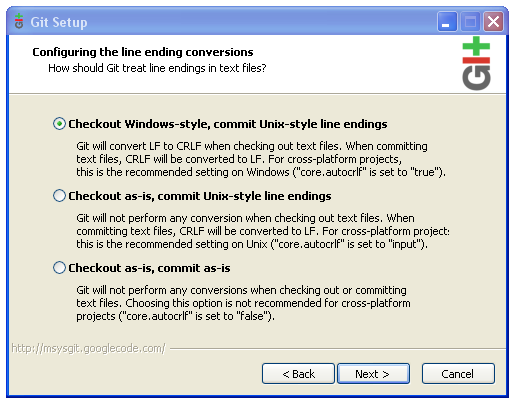
The default settings should be OK.
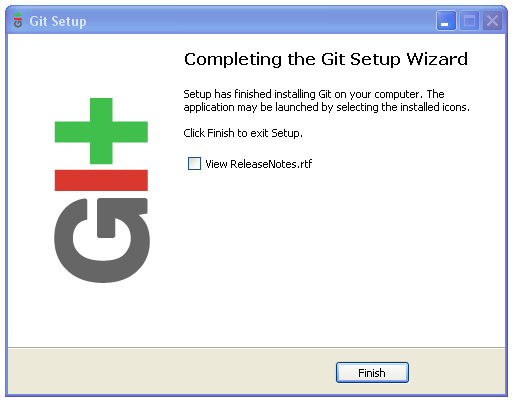
Git Installation is complete! Let's move on to TortoiseGit.
TortoiseGit?
Run TortoiseGit-1.7.11.3-32bit.msi (or TortoiseGit-1.7.11.3-64bit.msi if you're on a 64-bit system) to begin TortoiseGit installation
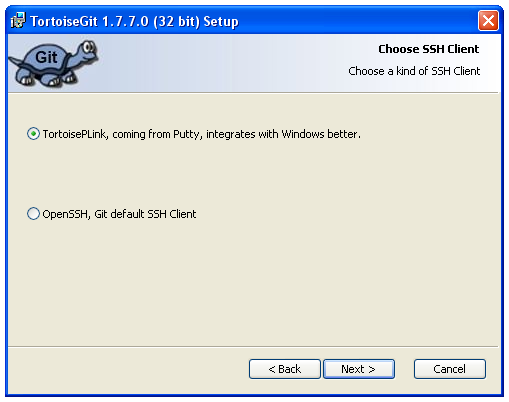
Once again, the default options should be OK.
TortoiseGit installation is complete! Let's move on to creating your public/private key pair.
Public/Private Key Creation
Browse to the folder where you installed TortoiseGit. By default, this will be C:\Program Files\TortoiseGit\
Open the bin folder inside the TortoiseGit? folder and located puttygen.exe
Run puttygen.exe
Click the 'Generate' button. You'll be asked to move your mouse around for a bit while a progress bar fills up. This helps make your key more random (which makes it harder for someone else to impersonate you).
When the progress bar finishes, your key will appear. Enter a password (twice) before continuing.
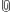
First click 'Save Public Key' and save your key somewhere. I've saved mine as 'public.ppk' in my Application Data/ssh folder, but you can put this anywhere. Just keep it somewhere safe where you can find it later.
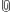
Next click 'Save Private Key' and save your key somewhere. I recommend putting it in the same place as your public key. I've named mine 'private.ppk'. Remember: your private key never leaves your computer! Only your public key gets shared with anyone.
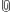
Now that you've saved your public/private key pair, copy the 'Public key for pasting into OpenSSH authorized_keys file. Don't worry about what that means; we're going to be emailing this to David/Rom? instead.
Conclusion
Congratulations You've successfully:
- Installed Git and TortoiseGit
- Set up your Public/Private key pair
Attachments (16)
- file-list.png (8.8 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
- git-1.png (19.7 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
- git-2.png (27.4 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
- git-6.png (17.5 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
- tortoisegit-1.png (67.4 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
- tortoisegit-2.png (32.2 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
- tortoisegit-3.png (68.5 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
- git-3.png (24.9 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
- git-4.png (25.9 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
- git-5.png (17.5 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
-
git_clone_boinc.jpg (51.4 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Shows how to add the URL to the program
-
git_clone_select.jpg (36.0 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Shows how to select the initial clone
-
git_pull_menu.jpg (35.7 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Using the Git Pull command from RC-,menu
-
git_pull_window.jpg (43.7 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Shows Git Pull window, which URLs/commands to use.
-
git_pull_updating.jpg (31.5 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Shows Git Pull updating
-
git_pull_updated.jpg (50.9 KB) - added by 13 years ago.
Shows Git Pull updated
Download all attachments as: .zip