| Version 20 (modified by , 12 years ago) (diff) |
|---|
Building BOINC on Unix
The BOINC software consists of several components:
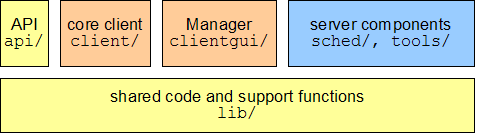
- Miscellaneous: the API and various shared code.
- Client: the core client and Manager.
- Server: the scheduler, file upload handler, daemons, and tools.
On UNIX systems, the BOINC software can be built by typing
./_autosetup ./configure [see options below] make
in the top directory.
- If you're creating a project, you need to build the server and miscellaneous software (you don't need to build the client software; participants can get that from the BOINC web site). Use
./configure --disable-client --disable-manager
- If you're porting the BOINC client software to a new platform, you need the client and miscellaneous components. Use
./configure --disable-server
- If you're developing or porting a BOINC application, you need only the miscellaneous component. Use
./configure --disable-server --disable-client --disable-manager
Configuration
Usage:
./configure [OPTION]... [VAR=VALUE]...
You can use environment variables to override the choices made by configure or to help it to find libraries and programs with nonstandard names/locations. To assign environment variables (e.g., CC, CFLAGS...), specify them as VAR=VALUE. Example: to compile BOINC with strict compiler warnings, use
./configure CXXFLAGS="-Wall -W -Wshadow -Wpointer-arith -Wcast-qual -Wcast-align -Wwrite-strings -fno-common "
Defaults for the options are specified in brackets.
Configuration
| -h, --help | display configuration options and exit |
| --with-boinc-platform=NAME | Override the BOINC platform name determined by autoconf. i.e. Use NAME as platform to compile into the client. Only necessary if configure does not recognize your platform correctly by default. You can check the platform after the configure step by looking at the value of the HOSTTYPE variable in config.h |
| --with-boinc-alt-platform=NAME | Use this option to build an client that supports an alternate platform name. For example, on a x86_64 linux system that supports both 64 bit and 32 bit executables, you might specify --with-boinc-platform=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu and --with-boinc-alt-platform=i686-pc-linux-gnu. |
Installation directories
| --prefix=PREFIX | install architecture-independent files in PREFIX [/usr/local] By default, make install will install all the files in /usr/local/bin, /usr/local/lib etc. You can specify an installation prefix other than /usr/local using --prefix, for instance --prefix=. For better control, use the options below.
|
Optional Features
| --disable-FEATURE | do not include FEATURE (same as --enable-FEATURE=no) |
| --enable-FEATURE[=ARG] | include FEATURE [ARG=yes] |
| --enable-debug | enable tracing and debugging flags for all components (alternatively, include -g in CFLAGS and CXXFLAGS) |
| --disable-server | disable building the server component |
| --disable-manager | disable building the manager component (Disabled automatically if configure can't find wxWidgets) |
| --disable-client | disable building the client component Default: --enable-server --enable-client --enable-manager: builds server, client and manager. |
| --enable-shared[=PKGS] | build shared libraries [default=yes] |
| --enable-static[=PKGS] | build static libraries [default=yes] |
| --disable-static-linkage | disable static linking of certain libraries |
| --enable-client-release | Try building a portable 'release-candidate' (currently implemented for Linux and Solaris only): this links libstd++ statically. You will probably need gcc-3.0 for this to produce a portable client-binary. It is therefore recommended to use CC=gcc-3.0 and CXX=g++-3.0 for this. (Default = no) |
Optional Packages
| --with-PACKAGE[=ARG] | use PACKAGE [ARG=yes] |
| --without-PACKAGE | do not use PACKAGE (same as --with-PACKAGE=no) |
| --with-x | use the X Window System |
| --with-apple-opengl-framework | use Apple OpenGL framework (Mac OS X only) |
| --with-wxdir=PATH | Use installed version of wxWidgets in PATH |
| --with-wx-config=CONFIG | wx-config script to use (optional) |
Environment variables
| CC | C compiler command |
| CFLAGS | C compiler flags |
| LDFLAGS | linker flags, e.g. -L<lib dir> if you have libraries in a nonstandard directory <lib dir> |
| CPPFLAGS | C/C++ preprocessor flags, e.g. -I<include dir> if you have headers in a nonstandard directory <include dir> |
| CXX | C++ compiler command |
| CXXFLAGS | C++ compiler flags. |
| CPP | C preprocessor |
| CXXCPP | C++ preprocessor |
| F77 | Fortran 77 compiler command |
| FFLAGS | Fortran 77 compiler flags |
| MYSQL_CONFIG | mysql_config program |
Source layout
The top-level Makefile.am contains the SUBDIRS= line which sets up directory recursion, and the rules for creating source distributions.
Each subdirectory's Makefile.am contains the rules for making the binaries and libraries in that directory and any extra files to distribute.
Usually you will want to run make from the top level (the directory containing the file configure), but sometimes it is useful to run make and make check in certain subdirectories (e.g. client/).
Adding new directories
If you create a new directory with another Makefile.am, you should
- make sure the directory is referenced by a
SUBDIRS=line from its parentMakefile.am - add it to the AC_CONFIG_FILES directive in
configure.ac.
Version number
To set the BOINC client version:
set-version 5.12.47
in the BOINC top-level source directory. This updates the AC_INIT line in configure.ac and regenerates files that use the version numbers (config.h, py/version.py, test/version.inc, client/win/win_config.h, Makefiles)
Attachments (1)
-
components.png (3.4 KB) - added by 18 years ago.
Software components
Download all attachments as: .zip
