| Version 24 (modified by , 17 years ago) (diff) |
|---|
Bolt Tutorial, Part I: Courses and Lessons
Creating a course
Install the BOINC software on a Linux system and run configure (you don't need to make). Or run the BOINC server virtual machine in a VMWare player on any computer.
Use make_project to create a BOINC project named "test":
> cd boinc/tools > make_project --web_only test
Read ~/projects/test/test.readme and do what it says.
Let's say your server's domain name is "a.b.c".
- Visit http://a.b.c/test/create_account.php and create an account for yourself.
- Visit http://a.b.c/test_ops/bolt_admin.php. Follow the instructions to create the Bolt database, then create a course named "Identifying California conifers" with short name "conifer1".
- Check out the Bolt example files:
svn co http://boinc.berkeley.edu/svn/trunk/bolt_examples
and move them to the corresponding subdirectories of ~/projects/test/html/.
Lessons and sequences
Our first example is a course consisting of 13 lessons. Each lesson consists of a PHP or HTML file. For example, the first lesson is conifer_intro.php.
The course structure is defined by a "course document", trunk/bolt_examples/inc/conifer1.inc.
A course document is like an outline for the course; it is a hierarchy of units. The bottom-level unites are lessons and exercises. Each lesson is specified by:
lesson(
filename("file_name")
)
The higher-level units are Bolt control structures. In this example we use just one structure: sequence. The syntax for a sequence is:
sequence(
name("Name of the sequence"),
lesson(filename("Filename")),
[ ... other units ]
)
Bolt control structures can be nested: for example, the units in a sequence may include other sequences as well as lessons and exercises.
The course document is a PHP file. It must return a Bolt control structure. In this case, this is done as follows (lines 75-79):
return sequence(
name('course'),
intro_lessons(),
pine_lessons(),
cypress_lessons()
);
You can use the expressive power of PHP to simplify and organize your course document. For example:
- line 3: we include a separate file, conifer.inc, which defines page header and footer functions.
- lines 5, 23 and 49: we define functions intro_lessons(), pine_lessons() and cypress_lessons, each of which returns a sequence for a section of the course.
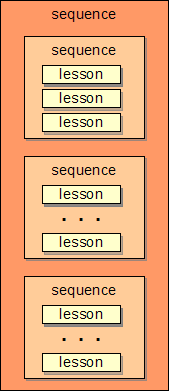
Diagramatically, the course structure is:
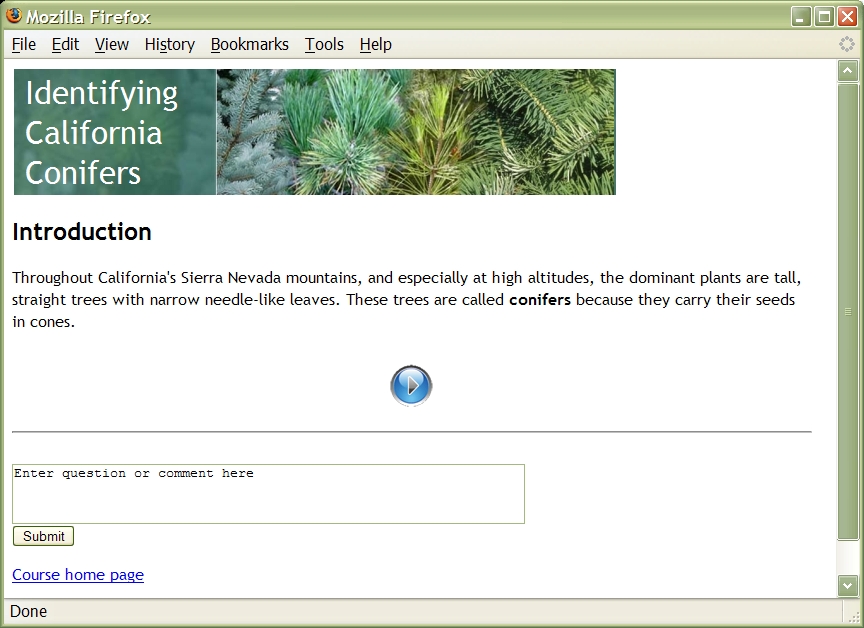
Now visit http://a.b.c/test/bolt.php. You'll be asked to log in; do so. Click on the button to start the course. Fill in the form asking for your demographic info. Then you'll see:
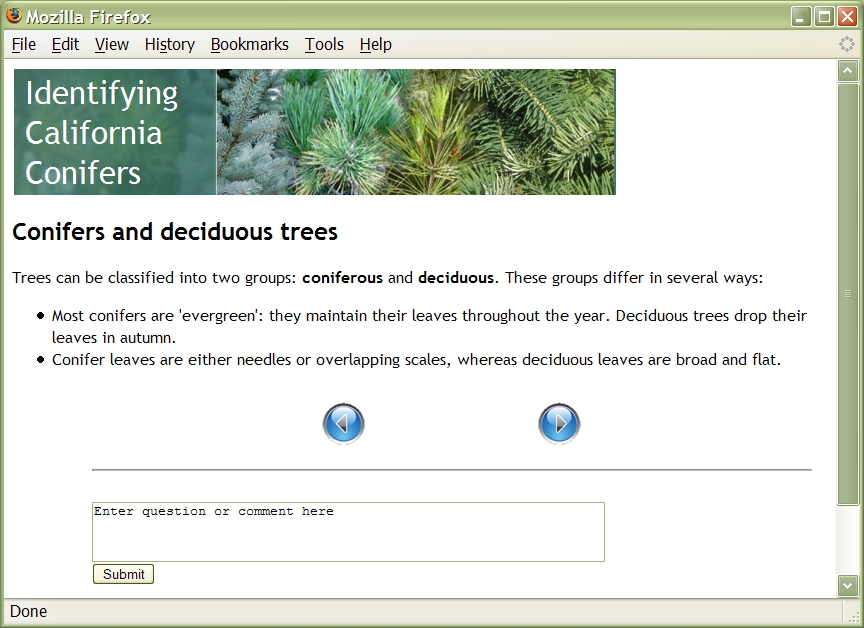
Note that below the lesson, Bolt has added some navigation links and a form to ask questions. Click on the "Next" button. You'll see:
Now suppose that instead of reading the lesson, you go away (for an hour or a month) and return. Simulate this by visiting http://a.b.c.test/bolt.php; click Resume. Notice that Bolt "remembers" where you are in the course (this is stored in the database; it will work even if you go to a different computer).
Attachments (5)
- bolt_l1.jpg (201.7 KB) - added by 18 years ago.
- bolt_l2.jpg (221.4 KB) - added by 18 years ago.
- bolt_history.jpg (144.5 KB) - added by 18 years ago.
- seq.png (4.9 KB) - added by 17 years ago.
- seq.2.png (4.9 KB) - added by 17 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip
