| Version 21 (modified by , 17 years ago) (diff) |
|---|
Bolt Tutorial, Part I: Courses and Lessons
Creating a course
Install the BOINC software on a Linux system, or run the BOINC server virtual machine in a VMWare player on any computer.
Use make_project to create a BOINC project named "test":
> cd boinc/tools > make_project --web_only test
Read ~/projects/test/test.readme and do what it says.
Let's say your server's domain name is "a.b.c".
- Visit http://a.b.c/test/create_account.php and create an account for yourself.
- Visit http://a.b.c/test_ops/bolt_admin.php. Follow the instructions to create the Bolt database, then create a course named "Identifying California conifers" with short name "conifer1".
- Copy the files from http://boinc.berkeley.edu/bolt_example to ~/projects/test/html/.
Lessons and sequences
Let's start with a simple course consisting of 13 lessons. Each lesson consists of a PHP or HTML file. The first lesson is conifer_intro.php:
<?php echo " <h2>California conifers</h2> Throughout California's Sierra Nevada mountains, and especially at high altitudes, the dominant plants are tall, straight trees called <b>conifers</b>. Conifers are remarkable in many ways: <ul> <li> They have existed in approximately their current form for 240 million years. <li> They display remarkable tenacity and adaptibility, managing to grow in the most unlikely places: <img src=jeffrey_pine.jpg> <p class=caption>A Jeffrey pine growing on granite in the High Sierra</p> <li> The largest living thing is a conifer: the General Sherman, a Giant Sequoia in Sequoia National Park. Its trunk volume is 52,500 cubic feet. <img src=general_sherman.jpg> <li> The oldest known living thing is a conifer: a 4,500-year-old bristlecone pine in the White Mountains (a mountain range that neighbors the Sierra Nevada). <img src=bristlecone-pine.jpg> <p class=caption>A bristlecone pine.</p> </ul> This course will teach you how to identify the most common types of California conifers. "; ?>
The course structure is defined by conifer1.php:
<?php
require_once("../inc/conifer.inc");
function intro_lessons() {
return sequence(
name('intro lessons'),
lesson(
title('Introduction'),
filename('conifer_intro.php')
),
lesson(
title('Conifers and deciduous trees'),
filename('conifer_decid.php')
),
lesson(
title('Conifers taxonomy'),
filename('taxonomy.html')
)
);
}
function cypress_lessons() {
return sequence(
name('Cypress genera'),
lesson(
title('Incense-Cedar'),
filename('incense-cedar.html')
),
lesson(
title('Juniper'),
filename('juniper.html')
),
lesson(
title('Coast Redwood'),
filename('coast-redwood.html')
),
lesson(
title('Giant Sequoia'),
filename('giant-sequoia.html')
),
lesson(
title('Red Cedar'),
filename('red-cedar.html')
)
);
}
function pine_lessons() {
return random(
name('Pine genera'),
lesson(
title('Pines'),
filename('pine.html')
),
lesson(
title('Spruces'),
filename('spruce.html')
),
lesson(
title('Douglas Fir'),
filename('douglas-fir.html')
),
lesson(
title('Hemlock'),
filename('hemlock.html')
),
lesson(
title('Firs'),
filename('fir.html')
)
);
}
return sequence(
name('course'),
intro_lessons(),
pine_lessons(),
cypress_lessons()
);
?>
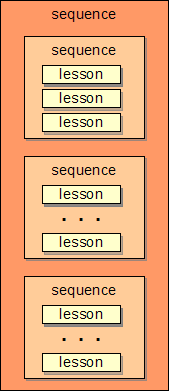
Diagramatically, the course structure is:
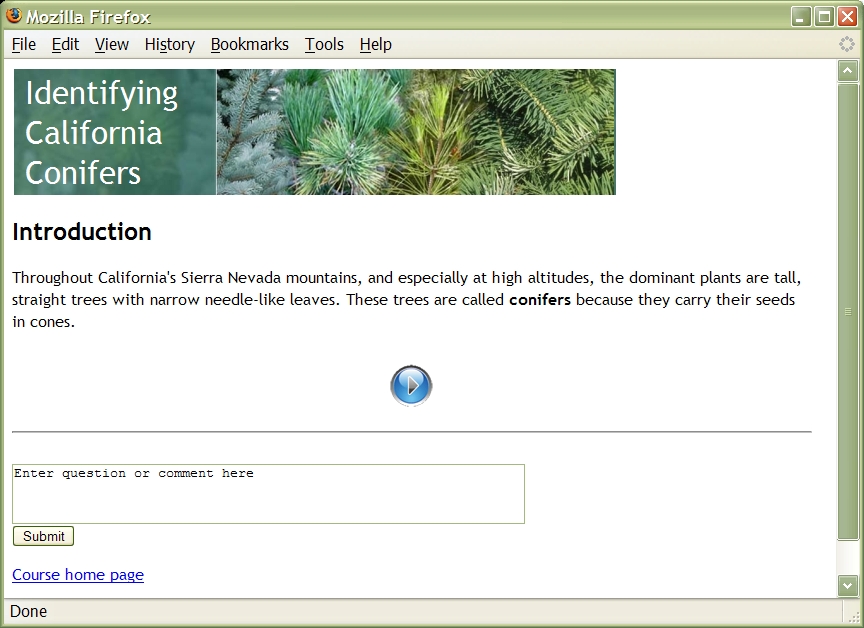
Now visit http://a.b.c/test/bolt.php. You'll be asked to log in; do so. Click on the button to start the course. Fill in the form asking for your demographic info. Then you'll see:
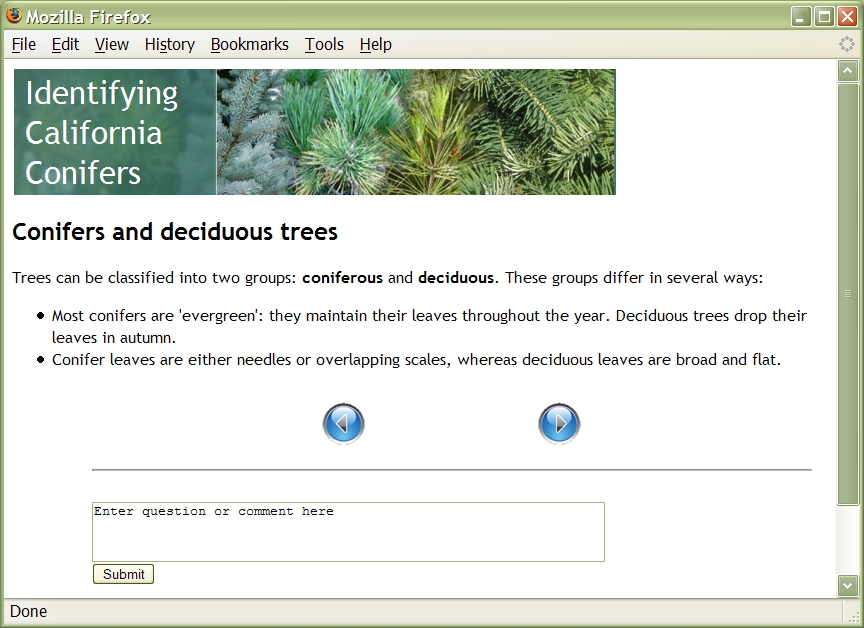
Note that below your lesson Bolt has added some navigation links and a form to ask questions. Click on the "Next" button. You'll see:
Now suppose that instead of reading the lesson, you go away (for an hour or a month) and return. Simulate this by visiting http://a.b.c.test/bolt.php; click Resume. Notice that Bolt "remembers" where you are in the course (this is stored in the database; it will work even if you go to a different computer).
Now visit http://a.b.c.test/bolt.php again, and click on "History". You'll see something like:
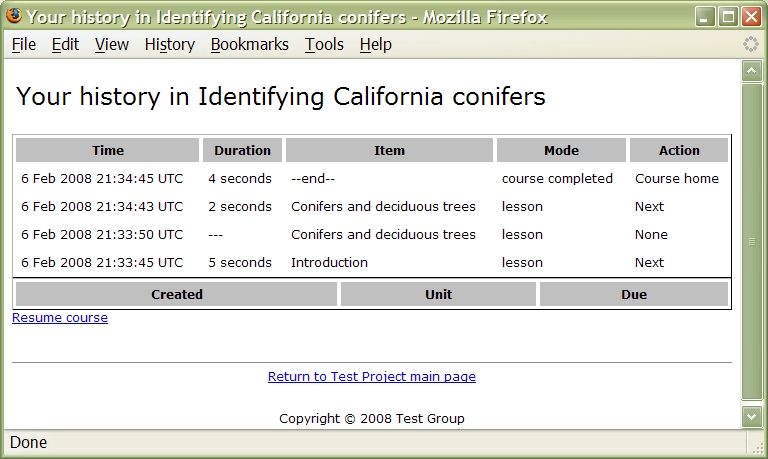
Bolt has recorded your course interactions and their timing, in its database; this is used for course analytics (see part III of this tutorial).
Attachments (5)
- bolt_l1.jpg (201.7 KB) - added by 18 years ago.
- bolt_l2.jpg (221.4 KB) - added by 18 years ago.
- bolt_history.jpg (144.5 KB) - added by 18 years ago.
- seq.png (4.9 KB) - added by 17 years ago.
- seq.2.png (4.9 KB) - added by 17 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip
